
Transcription
*Supplement #2 etc in previous blog comments welcomed
Name - Goehler
Reading Guide #3 for 2nd third of the semester
Interpersonal communication: theories of helping (cognitive/behavioral)
In preparation for the class discussion, please complete the following before class.
Look over pages 10-23, 168-169 in Supplement #2 (Cognitive Therapy by Judith Beck) & the Cognitive Distortions Supplement
1. What will you learn about in this reading guide?
Cognitive Therapy
Cognitive Distortions
Conceptualizing difficulties in cognitive terms, determines therapy
As you read pages 10-11, keep in mind that as a paraprofessional in human services, you will not be a therapist, but you will be using theoretical approaches to helping.
1. What are the author's key suggestions for those learning cognitive therapy?
In a nutshell; disfunctional thinking is common to all psychological disturbances. Realistic evaluation and modification of thinking produce improvement. Enduring improvement results from modification of dysfunctional beliefs. The therapist seeks to produce change in the thinking and belief system in order to change behavior
2. Connecting to past learning: How does this reading relate to self-awareness, self-development, metacognition, and emotional intelligence?
E1: Understanding yourself and relating to others, is a self-awareness built upon thinking about thinking. Cognitive awareness in self-development is a process wherein the experiential learning rewires how you think and correspondingly, what you do.
Self-reflection is key in CBT: Thinking about thinking.
Read pages 16-18
1. Define core belief
The most fundamental level of overgeneralized superficial, global and rigid thought patterns. Core beliefs influence development of -->
2. Define intermediate beliefs
Rules, attitudes, assumptions related to core beliefs. These beliefs influence perception of the situation and correspondingly influences thoughts, feelings and behaviors.
3. Define automatic thoughts
Cognitions closest to conscious awareness. Spring from beliefs and perception of events and influence behavior.
4. Describe the relationship between beliefs, thoughts, emotions, and behavior.
Underlying beliefs influence thoughts influence emotions influence behavior.
Read pages 19-23
1. List Sally's core belief, thoughts, emotions, and behaviors.
Helpless, defeated, overwhelmed, incompetent; thoughts of negative beliefs about herself made her feel inadequate, depressed - made he hypervigilant to succeed.
Name - Goehler
2. Write a concise summary of the case example about Sally.
Living in the shadow of an overachieving older sibling and degraded by mother, created inferiority complex prompting low self esteem in personal ambitions - causing depression and loneliness.
Read the lists of beliefs in supplement #4 (p. 16): these lists provide examples of core beliefs.
1. How would you define the category "helpless core beliefs?"
negative, self-defeating, disabling.
2. How would you define the category "unlovable core beliefs?"
negative, self-defeating, disabling
3. Personal application: As it relates to the past or present, give an example of a helpless or unlovable core belief that to emotions and some type of behavior in your life. *NOTE - you may need to work backward by beginning with the behavior.
A. List the core belief
I am defective
B. List the emotions
Apathy - who cares!
C. Explain the behavior.
Anything goes.
D. According to cognitive behavioral theory, how would you change the emotions and behavior?
Identify cause of core belief (exiled prisoner unwanted by society), re-consider helpless condition and re-determine course of actions necessary to reintegrate into society. Start with simple goals toward life goal.
Read the 11 cognitive distortions found in supplement #5 (p. 17).
Complete the chart located on the following pages by defining the distortion, describing a time you experience or observed someone using the
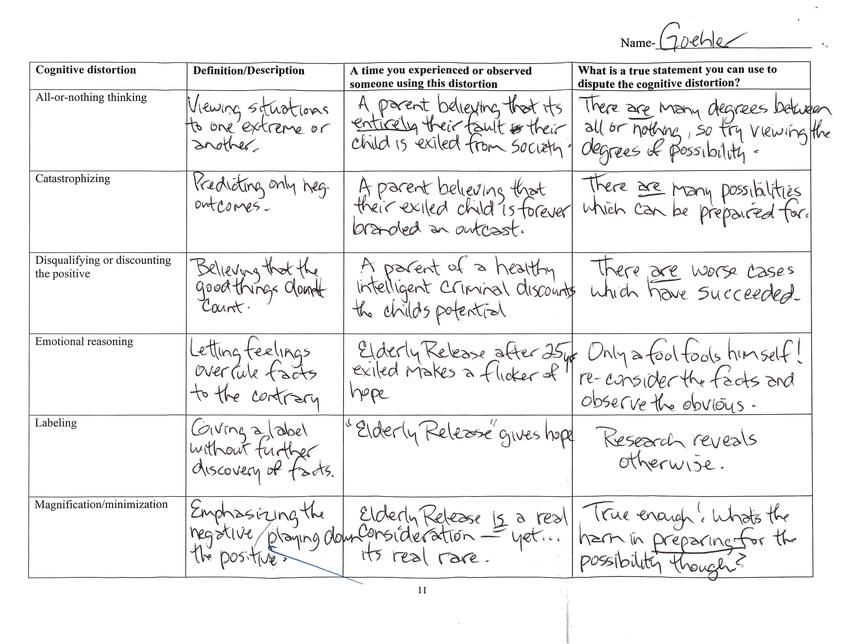
Cognitive Distortion - All-or-nothing thinking
Definition/Description - Viewing situations to one extreme or another.
A time you experienced or observed someone using this distortion - A parent believing that its entirely their fault their child is exiled from society.
What is a true statement you can use to dispute the cognitive distortion? - There are many degrees between all or nothing, so try viewing the degrees of possibility.
Cognitive Distortion - Catastrophizing
Definition/Description - Predicting only neg. outcomes
A time you experienced or observed someone using this distortion - A parent believing that their exiled child is forever branded an outcast
What is a true statement you can use to dispute the cognitive distortion? - There are many possibilities which can be prepared for.
Cognitive Distortion - Disqualifying or discounting the positive
Definition/Description - Believing that the good things don't count.
A time you experienced or observed someone using this distortion - A parent of a healthy intelligent criminal discounts the child's potential
What is a true statement you can use to dispute the cognitive distortion? - There are worse cases which have succeeded.
Cognitive Distortion - Emotional reasoning
Definition/Description - Letting feelings overrule facts to the contrary
A time you experienced or observed someone using this distortion - Elderly release after 25yrs exiled makes a flicker of hope
What is a true statement you can use to dispute the cognitive distortion? - Only a fool fools himself! Re-consider the facts and observe the obvious.
Cognitive Distortion - Labeling
Definition/Description - Giving a label without further discovery of facts.
A time you experienced or observed someone using this distortion - "Elderly Release" gives hope
What is a true statement you can use to dispute the cognitive distortion? - Research reveals otherwise
Cognitive Distortion - Magnification/minimization
Definition/Description - Emphasizing the negative/playing down the positive
A time you experienced or observed someone using this distortion - Elderly Release is a real consideration - yet... its real rare.
What is a true statement you can use to dispute the cognitive distortion? - True enough! What's the harm in preparing for the possibility though?
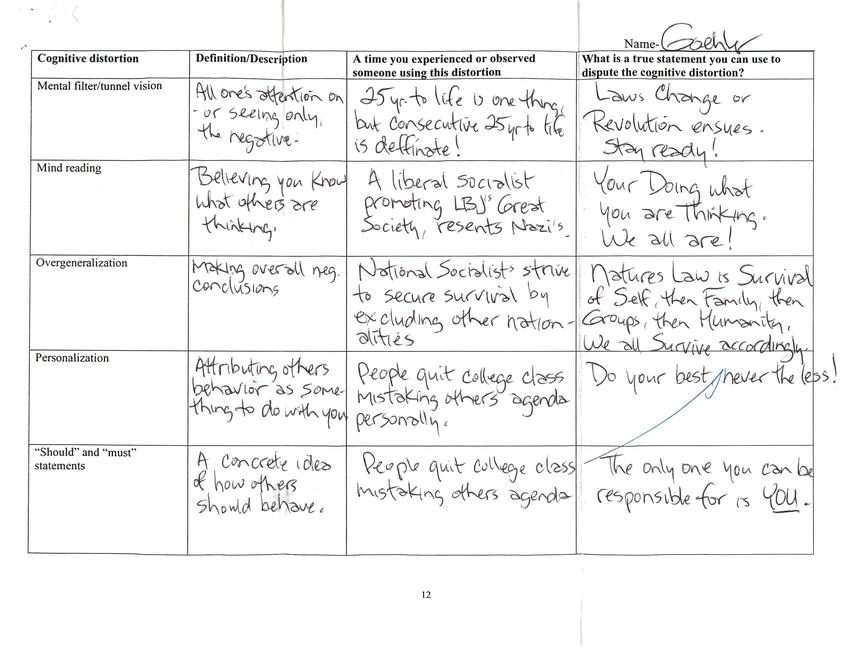
Cognitive Distortion - Mental filter/tunnel vision
Definition/Description - All one's attention on or seeing only the negative.
A time you experienced or observed someone using this distortion - 25 yr. to life is one thing, but consecutive 25 yr to life is definite!
What is a true statement you can use to dispute the cognitive distortion? - Laws change or revolution ensues - stay ready!
Cognitive Distortion - Mind reading
Definition/Description - Believing you know what others are thinking.
A time you experienced or observed someone using this distortion - A liberal socialist promoting LBJ's Great Society, resents Nazi's.
What is a true statement you can use to dispute the cognitive distortion? - Your doing what you are thinking. We all are!
Cognitive Distortion - Overgeneralization
Definition/Description - Making overall neg. conclusions
A time you experienced or observed someone using this distortion - National Socialists strive to secure survival by excluding other nationalities
What is a true statement you can use to dispute the cognitive distortion? - Natures law is survival of self, then family, then groups, then humanity. We all survive accordingly.
Cognitive Distortion - Personalization
Definition/Description - Attributing others behavior as something to do with you
A time you experienced or observed someone using this distortion - People quit college class mistaking others agenda personally.
What is a true statement you can use to dispute the cognitive distortion? - Do your best, never the less!
Cognitive Distortion - "Should" and "must" statements
Definition/Description - A concrete idea of how others should behave.
A time you experienced or observed someone using this distortion - People quit college class mistaking others agenda
What is a true statement you can use to dispute the cognitive distortion? - The only one you can be responsible for is YOU.
The Helping Relationship & Theories of Helping
The Helping Relationship
- Human Service Professionals believe the relationship is NECESSARY for helping to occur
- Similarities to other relationships
- 2 or more individuals are involved
- Involves communication and interaction
- Goes through developmental changes
- Differences from other relationships
- Power and potential for facilitating change
- One person is a professional helper, who utilizes skills and relational expertise
Client relationship development
-1. Coming together: developing and building a helping alliance also called rapport
-2. Exploring together: reconnaissance involves understanding the client's concerns, motivations, etc.
-3. Acting together: intervention involves actions by helper and/or helpee that lead to change
-4. Ending together: solidifying learning and making plans for ongoing growth ***NOTE-this is not in the book***
let's talk.
change
When is change needed?
How do people change?
What does the helper do?
Theories of helping
-Different perspectives on
- Explanations of when change is needed/when human behavior is healthy & unhealthy
- How people change
- The role and actions of the helper
Person-Centered Theory of Helping
- Creator: Carl Rogers
- Healthy vs. unhealthy:
- Healthy people:
- self-concept "the organized, consistent set of perceptions and beliefs about oneself" includes thoughts, values, and actions.
- congruent self-concept: alignment of the real and ideal self
- self-actualized (functioning as their optimum self
- Unhealthy people:
- disconnect between real and ideal self
- Time focus: present (here and now)
Person-Centered Theory of Helping
- Change: self-actualization occurs when people are in a relational environment that allows them to grow into their ideal selves.
- Role of the helper: create healthy environment
- Actions of the helper: use active listening to demonstrate facilitative conditions
- Genuineness/realness/congruence
- Acceptance/caring/prizing = unconditional positive regard
- Empathetic understanding
Reflection
- Reactions to this theory:
- Feelings
- Thoughts
- Application of this theory:
- Explain a time when you witnessed this theory working.
- Explain a time when you witnessed this theory not working.
- Describe a time when you experienced this theory as a helpee (with professional or personal).
- What aspects of this theory might you use as a helper?
We do not learn from experience... we learn from reflecting on experience.
- John Dewey
Other posts by this author
|
2023 may 31

|
2023 apr 5

|
2023 mar 19

|
2023 mar 5

|
2023 mar 5

|
2023 mar 5

|
More... |





Replies